

Welcome to the ASU Core Facilities Newsletter. We are ready to support all your research goals. Please follow our LinkedIn page for additional resources and community information.

Arizona State University has established itself as a trailblazer in innovation, holding the distinguished title of #1 in the U.S. for innovation for several consecutive years. One crucial factor contributing to this success is the significant impact of ASU's Core Research Facilities. These cutting-edge facilities have revolutionized the university's research capabilities, providing state-of-the-art resources and expertise across a wide range of disciplines.
With access to advanced instrumentation, specialized technical support and a diverse community of scholars, ASU researchers have been able to push the boundaries of knowledge, develop innovative solutions and address society's most pressing challenges.
How ASU maintains its top status.
News
Accelerating Arizona's Semiconductor Industry with the Materials-To-Fab Center
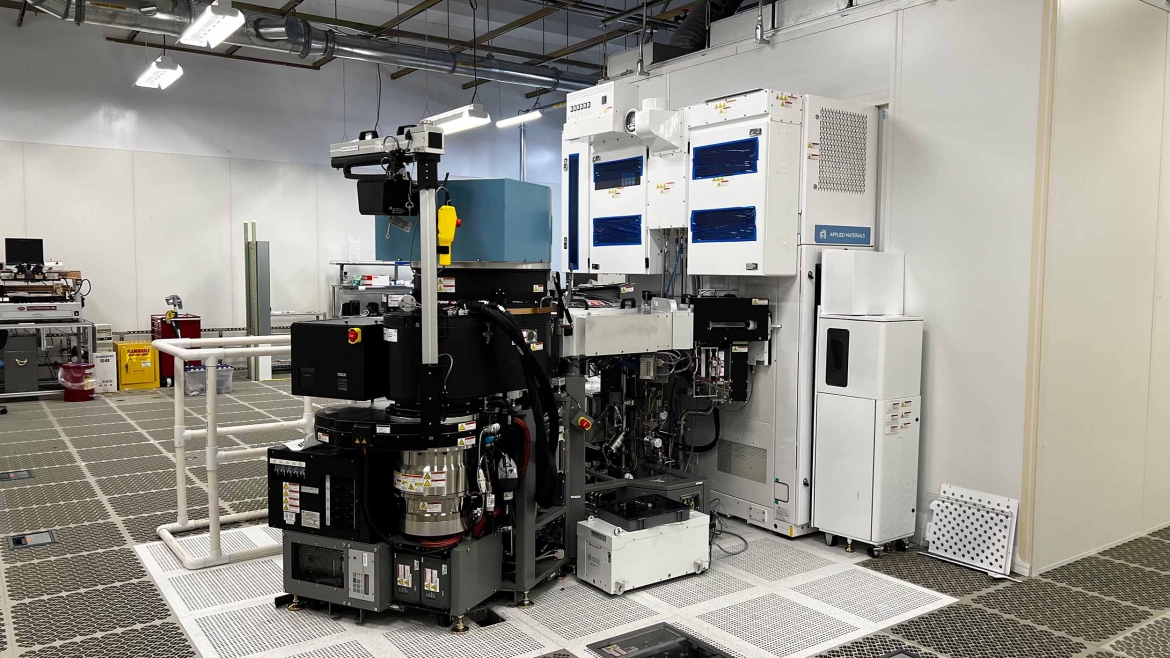

Arizona State University and Applied Materials Inc. have announced a groundbreaking alliance supported by the Arizona Commerce Authority, bringing more than $270 million to establish the Materials-to-Fab (MTF) Center. This state-of-the-art facility, housed in ASU's MacroTechnology Works, will serve as a collaborative environment where ASU, Applied Materials, industry partners, startups, government entities and academic institutions can work together. It aims to accelerate the transformation of innovative ideas into semiconductor prototypes using cutting-edge equipment.
For more details on this exciting initiative and its impact on Arizona's microelectronics industry.
Collaboration leads to New Test Engineering Curriculum
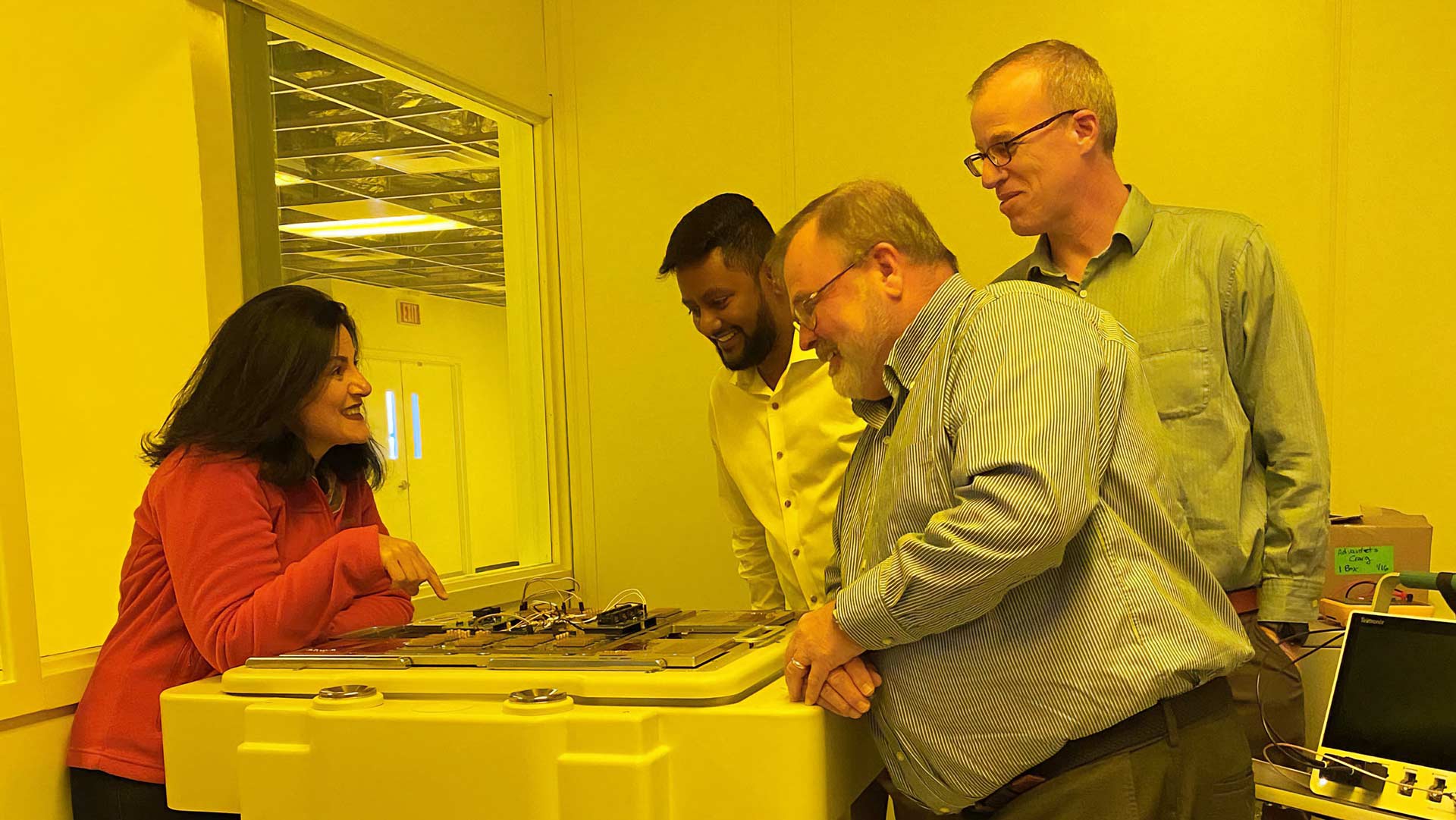

Leading semiconductor test equipment supplier Advantest Corporation and Arizona State University announced their collaboration with global semiconductor company NXP Semiconductors to create a new, ‘first-of-its-kind’ test engineering course at ASU.
The Advanced Electronics and Photonics Core Facility houses equipment that students can use for 'first-hand' experience in this course.
Why this curriculum is important.
SAXS Xenocs Xeuss 3.0 Installation
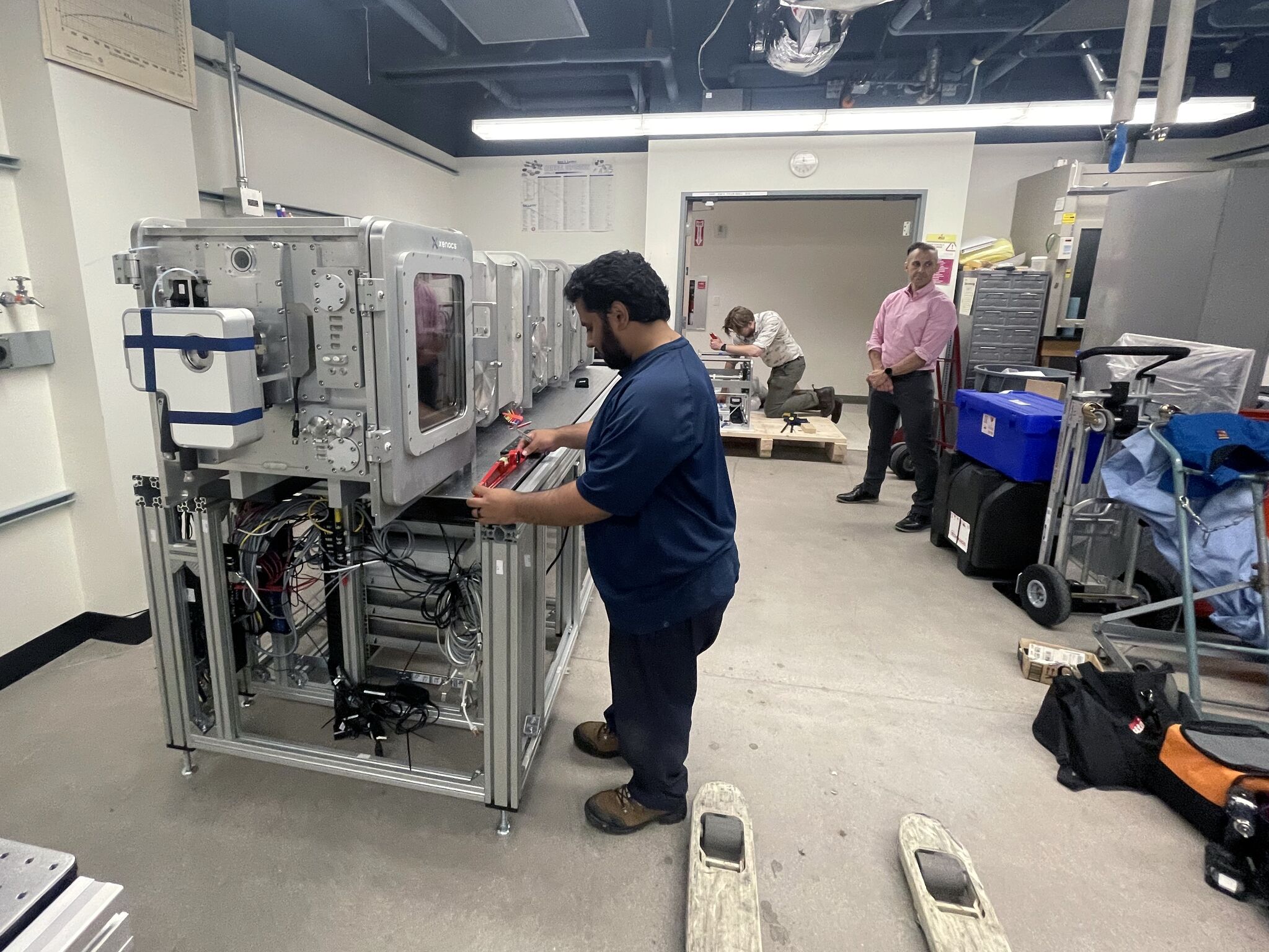

We are thrilled to announce the arrival and installation of our newest addition to the Eyring Materials Center: The Xenocs Xeuss 3.0 SAXS! This cutting-edge equipment is set to revolutionize the development of nanostructured materials with exceptional precision and versatility.
Serva Energy's Breakthrough: New Method to Produce Cancer-Killing Ac-225 Isotope
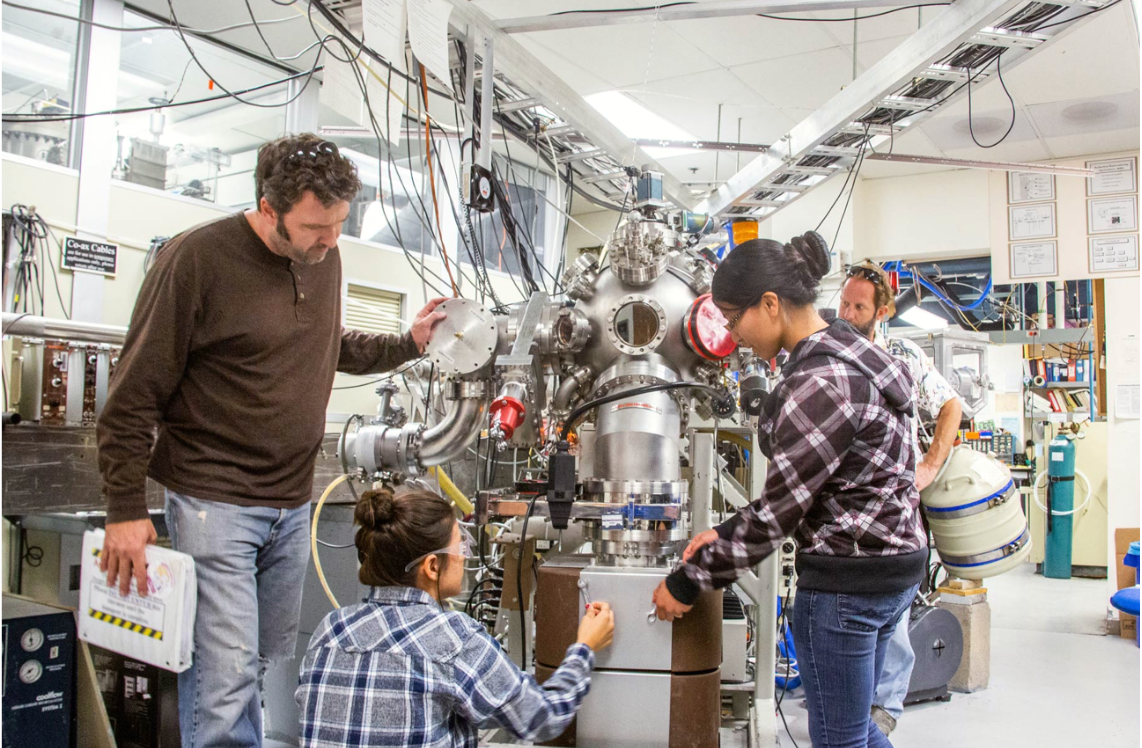

We are thrilled to unveil the groundbreaking achievements of Arizona State University's Core Research Facilities and the Eyring Materials Center in the realm of medical isotope production. Our efforts have contributed to the Serva Energy’s successful nuclear reactor-based transmutation of radium into the highly valuable and vital medical isotope actinium-225, with tremendous potential in cancer treatment.
Why this breakthrough is so important.
Videos
Who are we?
Heidelberg MLA-150
Rigaku SmartLab
Publications
Quantify and Reducing Ion Migration in Metal Halide Perovskites through Control of Mobile Ions
Researchers from the School of Electrical, Computer and Energy Engineering along with EMC and AEP Core Facilities quantify the ion migration of PSCs and MHP thin films in terms of mobile ion concentration (No) and ionic mobility (µ) and demonstrate that No has a more significant impact on device stability.
Understanding the Effect of Single Atom Cationic Defect Sites in an Al2O3 (012) Surface on Altering Selenate and Sulfate Adsorption
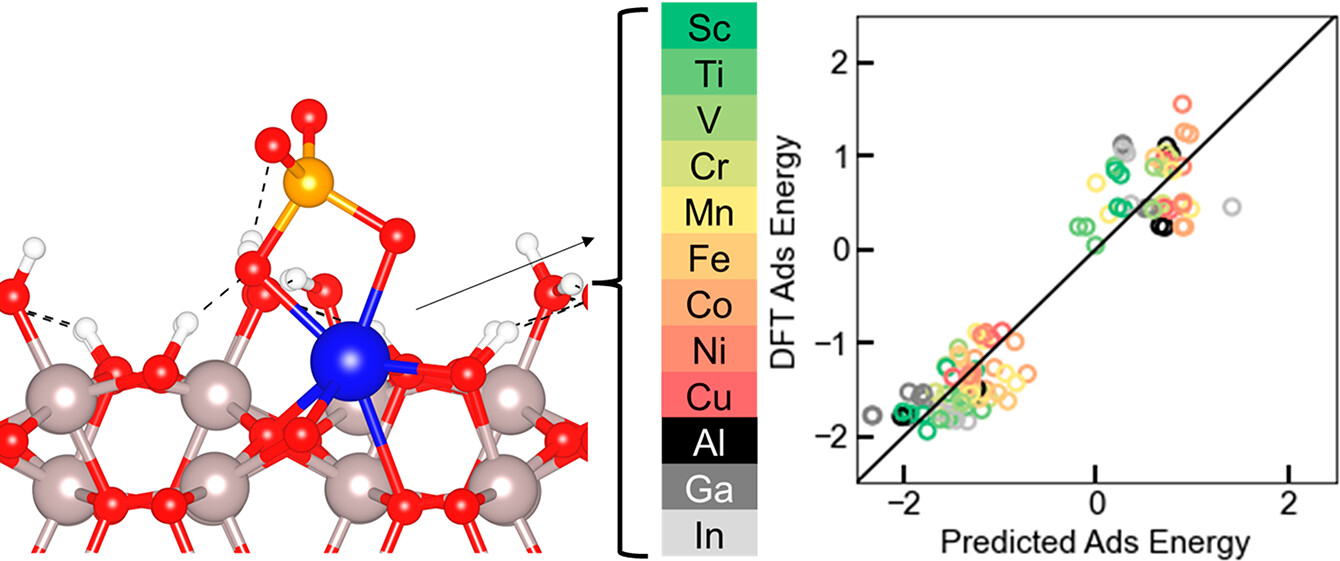
Researchers from the School of Engineering of Matter, Transport and Energy along with ASU's Research Computing discover that adsorption is a promising under-the-sink selenate remediation technique for distributed water systems. This study aims to show the relative importance of the water network effects and surface cation identity on controlling selenate and sulfate adsorption energy using density functional theory calculations.
What this means for water systems.

